Osteoporosis: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment Options
Kilani
February 24, 2025
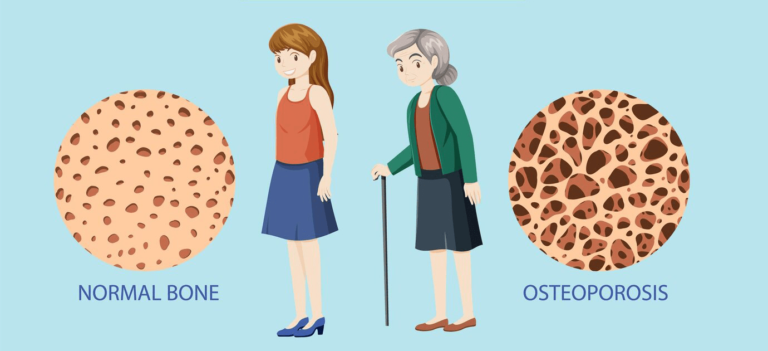
Osteoporosis Treatment and Prevention Introduction
Osteoporosis Treatment and Prevention is a condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. The name comes from the Greek words “osteo” (bone) and “poros” (porous), reflecting the porous nature of bones affected by this disease. It is often referred to as a “silent disease” because bone loss occurs without symptoms until a fracture happens. Although it is more commonly diagnosed in older adults, osteoporosis can develop in younger individuals as well.
Causes of Osteoporosis Treatment and Prevention
The primary cause of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone resorption (breakdown) and bone formation. When the body loses too much bone, or doesn’t make enough bone, bones become weak and brittle. There are several risk factors and causes associated with osteoporosis:
Age: Bone density peaks in the 20s, and after the age of 35, the rate of bone loss begins to exceed the rate of bone formation, contributing to osteoporosis as people get older.
Gender: Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis, particularly after menopause when estrogen levels decrease, affecting bone density.
Genetics: A family history of osteoporosis or fractures increases the risk. A history of low bone mass in parents, especially mothers, may raise the likelihood of developing osteoporosis.
Hormonal Changes: In addition to menopause-related estrogen loss, other hormonal changes such as thyroid disorders or excess cortisol (often due to long-term use of corticosteroids) can lead to osteoporosis.
Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of calcium and vitamin D in the diet can hinder proper bone formation and lead to weaker bones.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Physical inactivity or lack of weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, or weightlifting, can lead to the loss of bone density.
Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, like steroids and some anticonvulsants, may increase the risk of osteoporosis by interfering with bone formation.
Chronic Conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and certain gastrointestinal disorders (such as celiac disease) can increase the risk of osteoporosis due to inflammation or malabsorption of nutrients.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis often develops without symptoms in its early stages, but as bones become increasingly weak, certain signs may emerge:
Fractures: Fragile bones can break easily, even with minor falls or injuries. Common fractures occur in the hip, wrist, or spine.
Back Pain: A fracture in the spine can lead to severe back pain. If vertebrae are affected, it can result in a loss of height or a stooped posture.
Loss of Height: Over time, weakened vertebrae may collapse, causing a decrease in overall height, which may be noticeable.
Postural Changes: A common symptom of osteoporosis is a stooped or hunched back (also known as kyphosis), caused by vertebral fractures.
Bone Pain: Although osteoporosis itself does not usually cause pain, fractures resulting from weakened bones can cause significant discomfort.
Prevention of Osteoporosis
In this we have important role as physiotherapists in education how to prevent this problem. In our kilani physiotherapy center we focus on educate all patients in different ages about osteoporosis and how to prevent.
Preventing osteoporosis involves strategies to maximize bone health throughout life. Some effective preventive measures include:
Adequate Calcium Intake: Calcium is essential for bone health. The recommended daily intake of calcium varies by age and gender, but generally ranges from 1,000 mg to 1,200 mg. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are good sources of calcium.
Vitamin D: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. Getting sufficient sunlight, consuming foods rich in vitamin D, or taking supplements can help maintain proper bone health.
Weight-Bearing Exercises: Activities like walking, jogging, dancing, and weightlifting stimulate bone growth and help maintain bone density.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption. Smoking and excessive alcohol can increase bone loss and decrease the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients.
Regular Bone Density Screenings: Regular screenings, especially for individuals at higher risk, can help detect osteoporosis early, allowing for timely intervention.
Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet with adequate nutrients, including magnesium, vitamin K, and phosphorus, is crucial for maintaining strong bones.
Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
Once osteoporosis is diagnosed, treatments focus on slowing bone loss, improving bone density, and preventing fractures. The following treatment options are commonly used:
Medications:
Bisphosphonates: These drugs, such as alendronate, ibandronate, and zoledronic acid, work by slowing down the rate of bone loss.
Denosumab: A monoclonal antibody that can help reduce bone resorption and improve bone strength.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): These medications, like raloxifene, can help maintain bone density in postmenopausal women.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Estrogen therapy may be used in some cases to reduce bone loss in postmenopausal women.
Teriparatide and Abaloparatide: These are synthetic forms of parathyroid hormone used to stimulate bone formation.
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements: If dietary intake is insufficient, supplements may be prescribed to ensure optimal calcium and vitamin D levels.
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to improve strength, balance, and flexibility are important for reducing the risk of falls and fractures. A healthcare provider may recommend a personalized exercise regimen.
How Physiotherapy Can Help with Osteoporosis
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing osteoporosis by helping individuals improve their strength, balance, posture, and overall mobility. Here’s how physiotherapy can help:
Bone Strengthening Exercises: Physiotherapists can design weight-bearing and resistance exercises to help stimulate bone formation and increase bone density. These exercises, such as walking, squats, and weightlifting, help strengthen bones and prevent further bone loss.
Fall Prevention: Physiotherapists can teach patients how to improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls. This might include exercises to improve postural control and stability.
Pain Management: Through specific exercises, heat/cold therapy, and manual therapy techniques, physiotherapists can help manage pain associated with osteoporosis-related fractures or spinal issues.
We focus in kilani physiotherapy center on using manual Therapy to reduce pain
Postural Training: Physiotherapy can address postural changes that often occur with osteoporosis, such as a hunched or stooped posture. Postural correction exercises help individuals maintain proper alignment and reduce strain on bones and muscles.
Joint Protection and Flexibility: Gentle stretching exercises can help maintain flexibility and mobility in joints affected by osteoporosis, ensuring better range of motion and reducing stiffness.
Education: Physiotherapists educate patients on lifestyle modifications, such as proper posture, safe ways to lift objects, and how to avoid activities that increase fracture risk.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis Treatment and Prevention is a serious health condition that leads to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures, but with early detection, prevention, and appropriate treatment, its impact can be minimized. A combination of proper nutrition, exercise, and medical intervention can significantly improve bone health and reduce fracture risk. Physiotherapy is a vital aspect of the management of osteoporosis, offering patients the tools and knowledge to enhance strength, balance, and mobility, and ultimately improve quality of life.
If you suffer from this condition, do not hesitate to contact us at our branches in Jordan and Dubai.
Learn more about our full range of medical services at Kilani Centers, your trusted partner in health and wellness.
