Piriformis Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Kilani
March 13, 2025
Piriformis Syndrome Introduction
Piriformis syndrome is a common neuromuscular condition we often treat at Kilani Physiotherapy Center. It occurs when the piriformis muscle compresses the sciatic nerve, causing pain, discomfort, and limited mobility. This syndrome is especially common among individuals who sit for long hours at work, such as in offices or digital marketing roles. You can also read about our approach to other musculoskeletal conditions that affect posture and daily movement.
Causes of Piriformis Syndrome
Piriformis Syndrome may arise due to various factors, including: Muscle overuse: Repetitive activities such as running, cycling, or prolonged sitting can cause strain on the piriformis muscle.
Trauma or Injury: A direct blow to the buttocks from a fall, accident, or sports injury can trigger muscle spasms and nerve compression.
Poor Posture and Biomechanics: Improper sitting, walking, or running mechanics can contribute to the development of the syndrome.
Muscular Imbalances: Weakness or tightness in surrounding muscles can lead to compensatory strain on the piriformis muscle. Inflammation or Swelling: Inflammatory conditions or excessive physical activity can cause the muscle to enlarge and press on the sciatic nerve.
Symptoms
ndividuals with piriformis syndrome may experience:
Pain in the Buttocks: A deep, aching pain in the gluteal region that may worsen with movement.
Radiating Sciatic Pain: Pain that travels down the back of the thigh and into the lower leg, mimicking sciatica.
Most of our patients in kilani physiotherapy center who have pirifoms syndrome mimicking of this problem and lumber disc because this type of pain but with clinical assessment we can know what is the cause of the pain.
Numbness and Tingling: Sensory disturbances in the affected leg due to nerve compression.
Difficulty Sitting or Walking: Discomfort that intensifies with prolonged sitting, standing, or engaging in physical activities.
Muscle Spasms: Involuntary contractions in the piriformis muscle leading to stiffness and limited mobility.
Prevention
Preventing piriformis syndrome involves incorporating healthy movement habits and muscle care, including:
Regular Stretching: Performing targeted stretches for the piriformis and surrounding muscles can prevent tightness and stiffness.
Strength Training: Strengthening the core and lower body muscles improves overall stability and reduces strain on the piriformis.
Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and exercising helps prevent muscle imbalances.
Gradual Progression in Activities: Avoiding sudden increases in physical activity intensity minimizes the risk of muscle overuse.
Adequate Warm-up and Cool-down: Preparing muscles before exercise and allowing proper recovery afterward reduces the risk of injury.
Treatment
Treatment strategies for piriformis syndrome focus on relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring normal function. Common approaches include:
Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing activities that aggravate symptoms can allow the muscle to heal.
Cold and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs can reduce inflammation, while heat therapy can relax muscle tightness.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may help alleviate symptoms.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises targeting the piriformis and surrounding muscles improve flexibility and prevent recurrence.
Manual Therapy: Massage, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy can help relieve muscle tension.
Injection Therapy: In severe cases, corticosteroid or botulinum toxin injections may be considered to relieve muscle spasms and inflammation.
The Pivotal Role of Physiotherapy in Treatment
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the effective management and rehabilitation of piriformis syndrome. Some key physiotherapy interventions include:
Assessment and Diagnosis: Physiotherapists conduct thorough evaluations to identify underlying biomechanical issues contributing to the syndrome.
Customized Exercise Programs: Personalized stretching and strengthening routines help restore muscle balance and function.
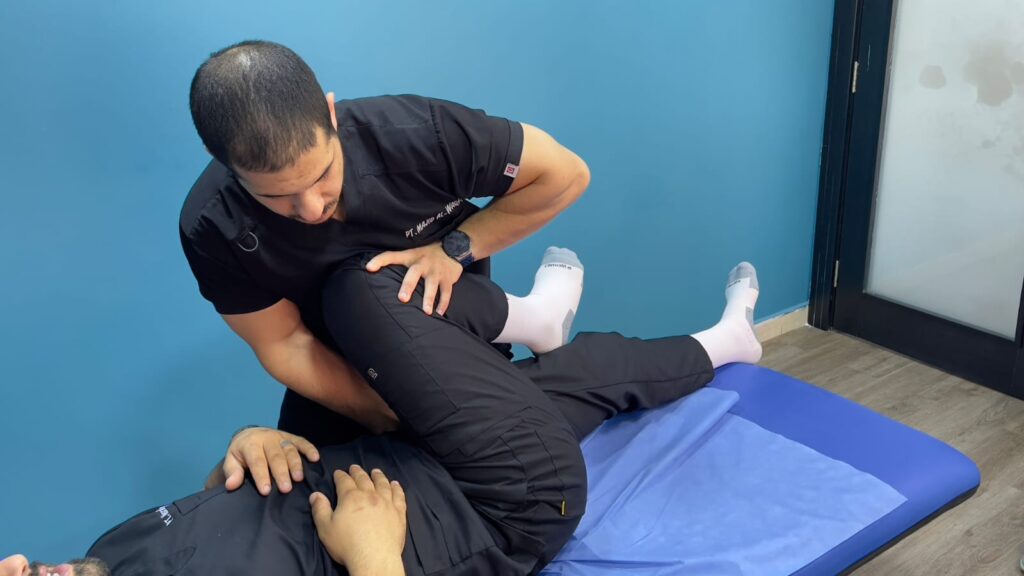
Manual Therapy Techniques: Techniques such as deep tissue massage, mobilization, and dry needling can alleviate muscle tightness and nerve compression.
In kilani physiotherapy center we focus on manual Therapy Techniques in treating this problem
Postural and Gait Training: Physiotherapists educate patients on proper posture and movement mechanics to prevent reoccurrence.
Electrotherapy and Modalities: Therapies like ultrasound and TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) can provide pain relief and reduce inflammation.
Conclusion
Piriformis syndrome is a debilitating condition that affects mobility and daily activities. Understanding its causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options is essential for effective management. Physiotherapy stands as a cornerstone in the rehabilitation process, helping individuals regain function, alleviate pain, and prevent recurrence through targeted interventions. By incorporating proper movement techniques, stretching, and strengthening exercises, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating piriformis syndrome.
If you suffer from this condition, do not hesitate to contact us at our branches in Jordan,Dubai and Sharjah.
